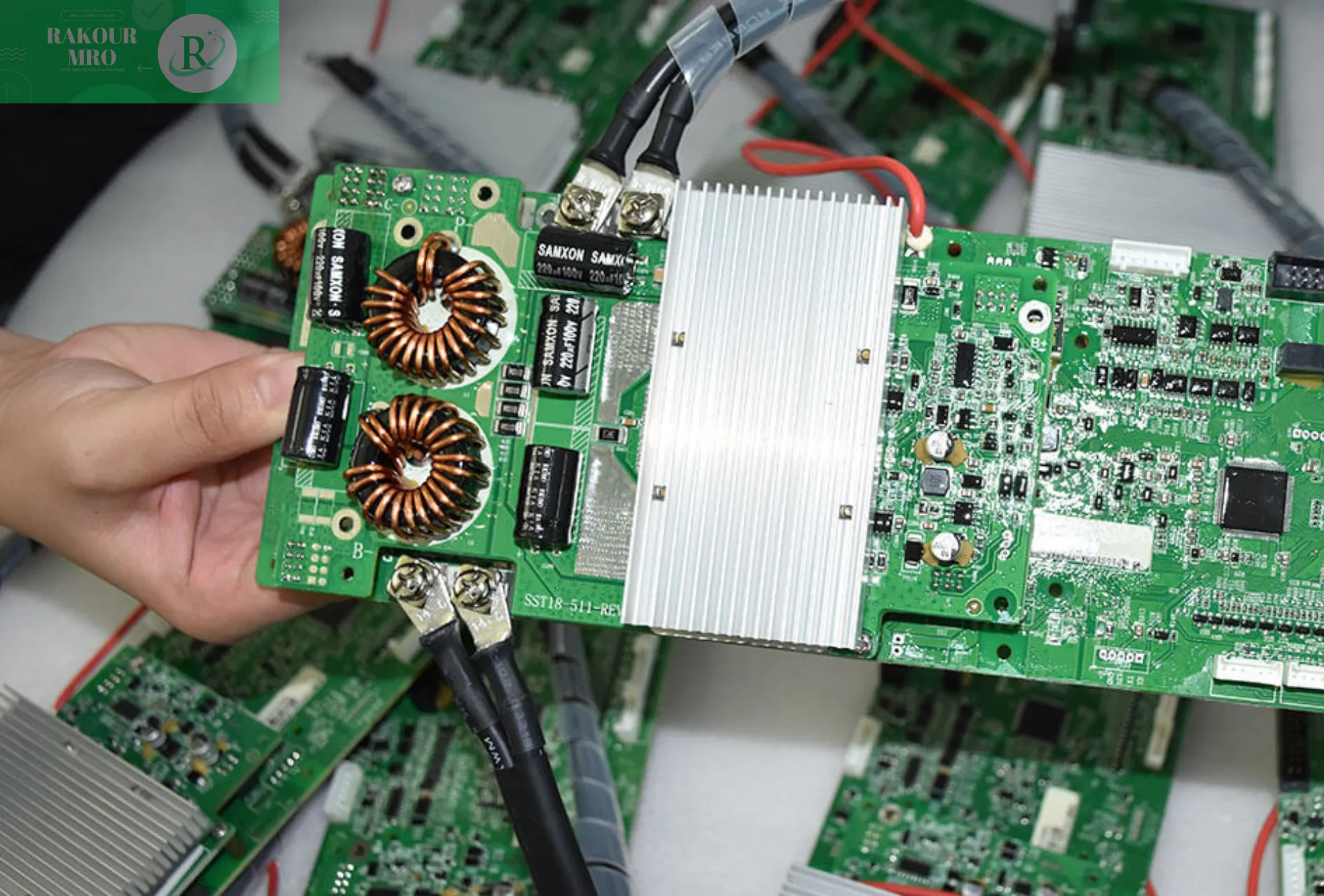
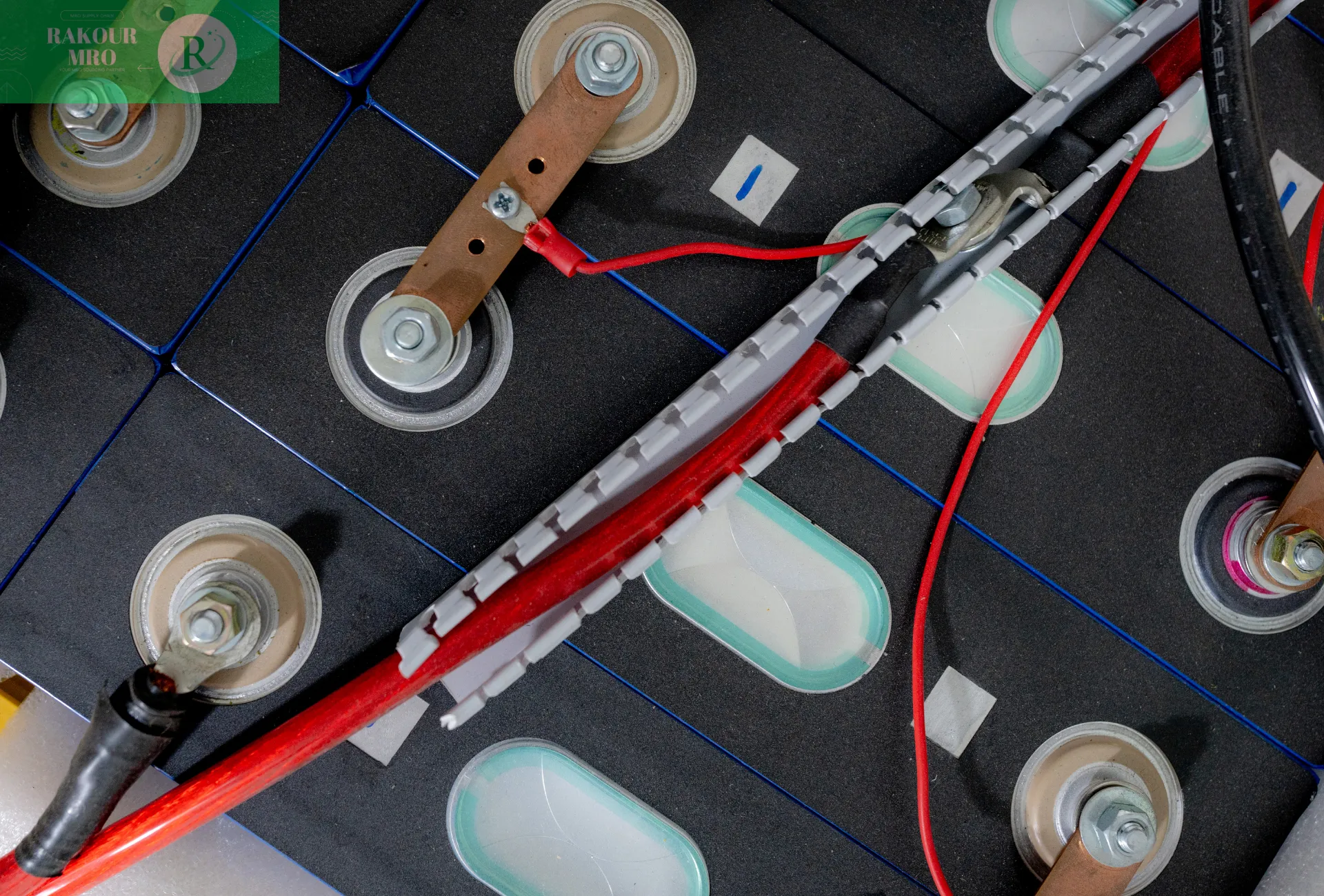
It is usually composed of a battery pack, mechanical components, heat exchange components, electronic control units, as well as necessary wiring harness, switching fuses and connectors. Its main function is to store and release electric energy through the mutual conversion of electrical energy and chemical energy.
Functions of the power battery system: engine start and stop, engine shutdown, brake energy recovery, torque assist, power assistance, oil-electric hybrid drive, direct electric power drive, etc.
Lead acid battery
It is mainly composed of lead and lead dioxide. Sulfuric acid is used as the electrolyte, and the materials used are relatively cheap.
Advantages: Stable voltage, cheap price.
Disadvantages: low energy density, short service life and frequent daily maintenance.
Traditional oil vehicles are actually equipped with batteries, usually lead-acid batteries, which are used to start the engine, provide instantaneous high current, and power the vehicle's low-voltage control system.
Nickel-hydrogen battery
Nickel-cadmium batteries (Ni-Cd) have been widely used earlier, but the "memory effect" is relatively serious, the derivation cycle life is short, and the pickaxe is a heavy metal and has strong toxicity. Therefore, nickel-hydrogen batteries (Ni-MH) came into being.
Advantages: High energy density (twice that of Ni-Cd), lighter than nickel pick batteries, longer service life, main and pollution-free to the environment; long cycle life, very small memory effect, and can be quickly charged.
Disadvantages: high cost, high self-discharge rate, still memory effect, low energy density, slow charge and discharge speed.
In fact, with the development of lithium-ion batteries, their performance has surpassed nickel-hydrogen batteries in all respects, so nickel-hydrogen batteries have only been glorious for a while.
lithium ion battery
In the 1990s, due to environmental protection, green and low-carbon became the main direction of energy development, among which wind energy, solar energy, etc. have achieved great development. The development of electric vehicles can achieve a "power-centered" energy consumption model transformation.
Working principle: A secondary battery (rechargeable battery) that mainly relies on lithium ions to move back and forth between the positive electrode and the negative electrode to work.
During charging and discharging, Li+ is embedded and de-inserted between the two electrodes (hence also known as "rock chair battery");
During charging, Li+ is deintercalated from the positive electrode and embedded into the negative electrode through the electrolyte, and the negative electrode is in a lithium-rich state;
During discharge, Li+ is deintercalated from the negative electrode and reintercalated into the positive electrode through the electrolyte.
Advantages of lithium-ion batteries: long life, large magnification, high energy density, and pollution-free (it surpasses nickel-hydrogen batteries in all respects, and has completely replaced nickel-hydrogen batteries in the field of power batteries).
The current bottlenecks of lithium-ion batteries: cost, cycle life, charging speed, safety, etc.