For traditional oil vehicles, the fuel tanks that provide energy involve fewer professional fields, while power batteries involve many fields (multi-discipline crossing), including electrochemistry, materials, machinery, electronics, software, fluids, heat transfer, etc. Its core technology mainly includes the following four aspects:
Machine: Mechanical properties
- The first consideration of power battery packs is mechanical properties. The PACK must have sufficient strength and stiffness, and will not cause deformation or abnormal function under vibration and impact loads, and will have sufficient protection in accidents such as collision, squeezing, rolling, and falling.
- The traditional MTP solution is like bringing a protective case to the mobile phone, which not only takes up space, but also makes it difficult to increase the PACK energy density. At present, mainstream PACK design solutions have gradually developed towards CTP solutions, and CTC solutions are also being further developed.
Electrical: Electronics and Electrical
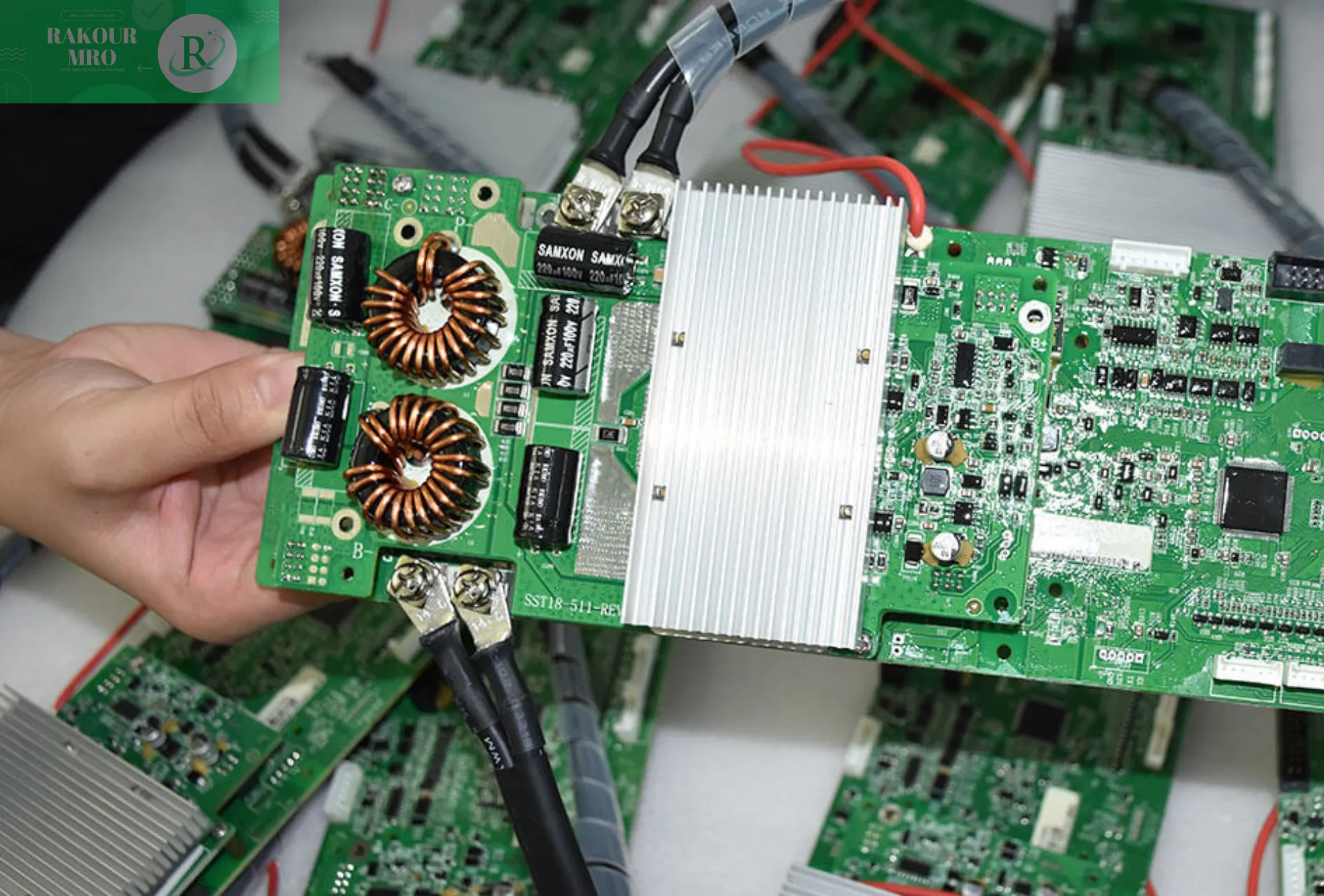
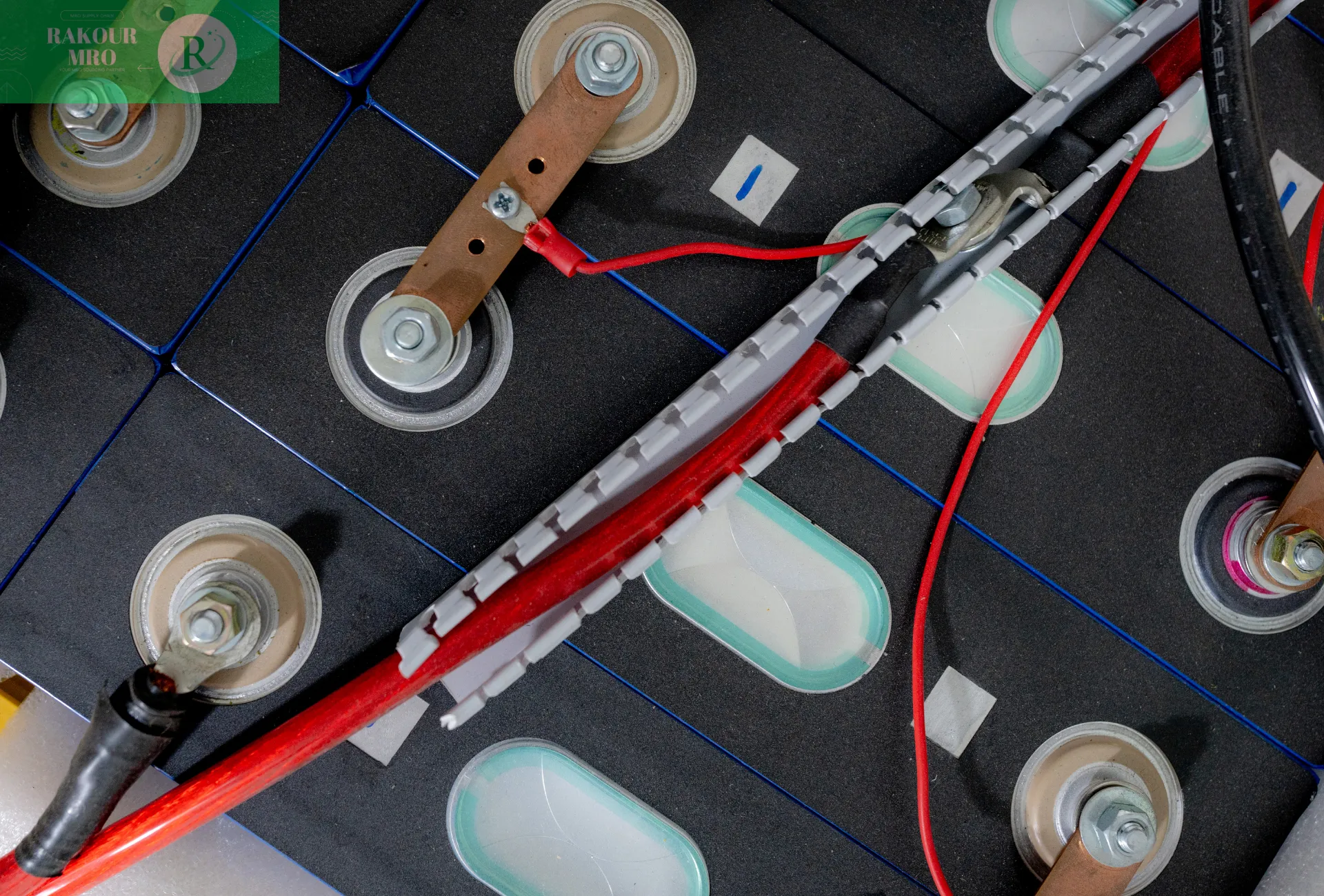
- Electrical: The instantaneous power of an electric vehicle can reach hundreds of kilowatts, the voltage ranges from tens of volts to hundreds of volts, and the current can also reach positive and negative hundreds of amperes. Therefore, there are very strict requirements for the cross-sectional area of the conductor, connection impedance, heating, insulation, aging, etc.
- Electronics: The battery management system (BMS) is required to collect the system’s voltage, current, temperature and other data, perform complex calculations, communicate with other components of the vehicle, complete specific functions, and judge the operating boundaries of the system in real time, control the abnormal state of the system, etc.
Thermal: Thermal management integration
Thermal management system needs to consider four aspects: heating, heat dissipation, heat insulation, and thermal balance.
Heat in winter; heat dissipation in summer. In short, ensure that the battery operates stably within a certain temperature range (optimal working range of 10~40℃)
Chemical: Electrochemical Mechanism
- The number of chemical reactions determines the charge and discharge energy of the battery (the number of electrons generated);
- The speed of chemical reactions determines the charging and discharging speed of the battery;
- The controllability and uncontrollability of chemical reactions determine the safety of the battery;
- The reversible degree of chemical reactions determines the life of the battery.