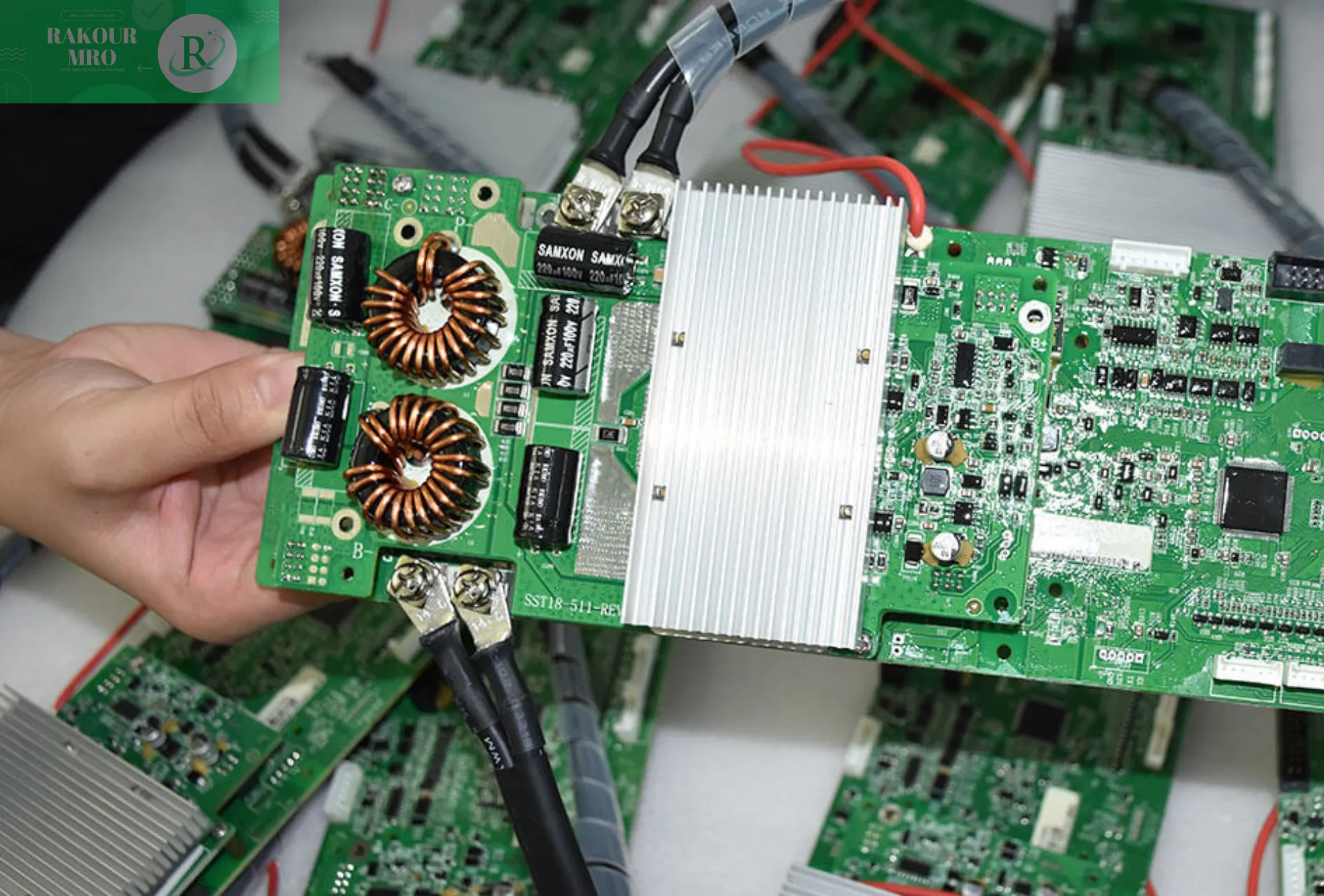
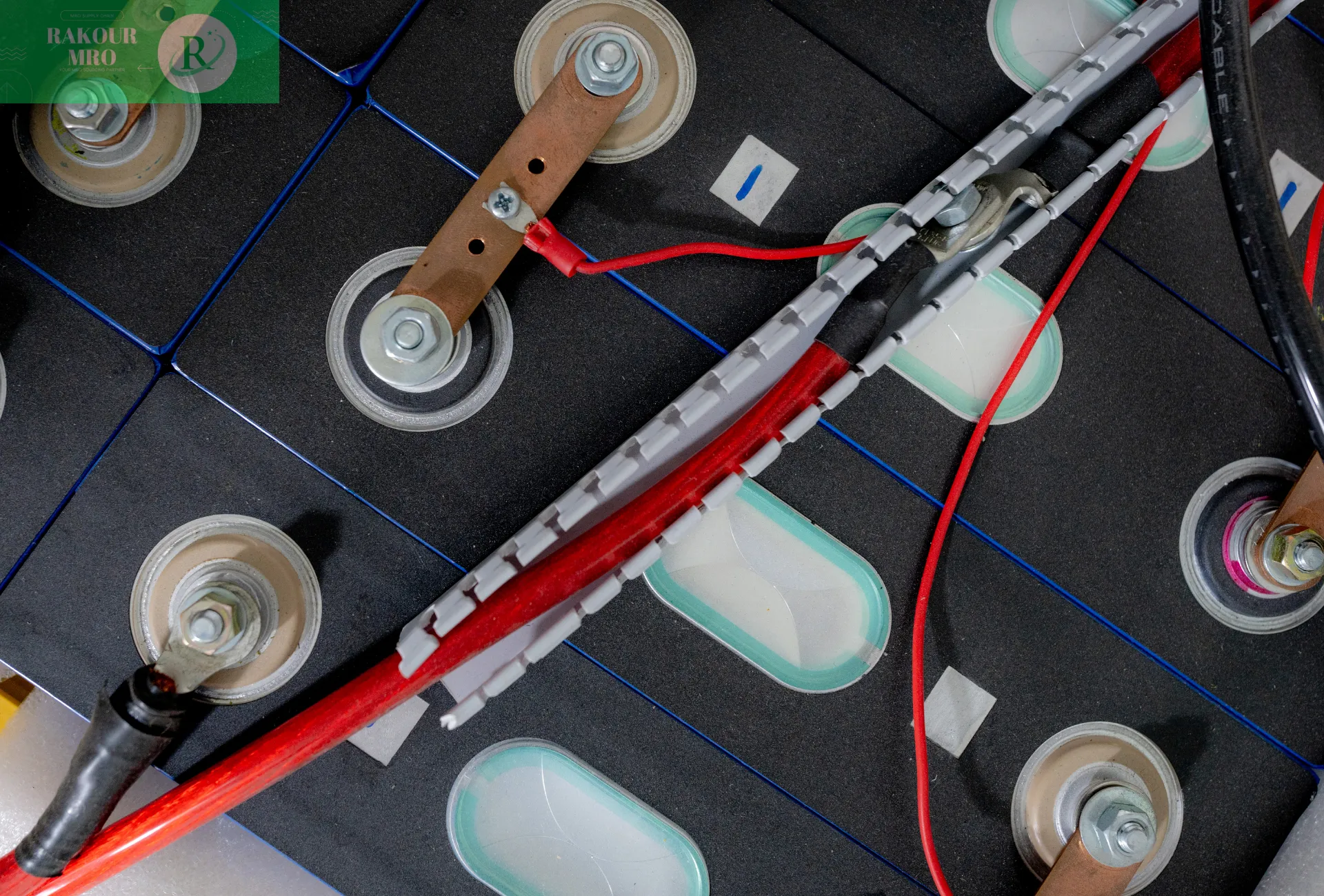
The Battery Management System (BMS) is an integral part of modern battery applications. It monitors, manages, and optimizes battery pack performance to ensure safe and efficient operation. BMS plays a vital role in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and portable electronic devices. Its operating principles encompass multiple aspects, including battery status monitoring, balancing management, thermal management, and communication with external systems.
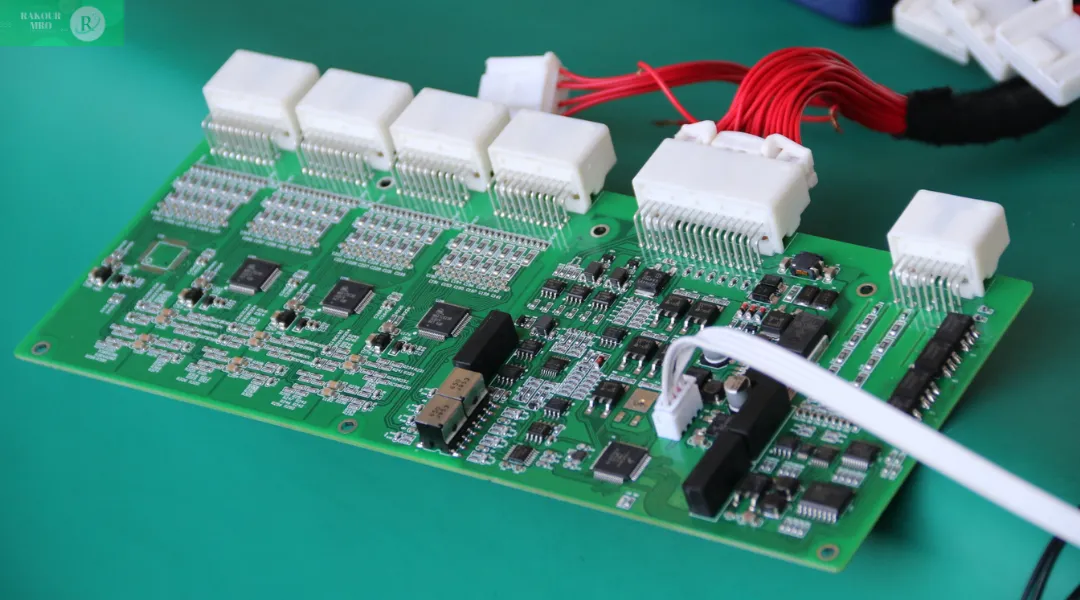
Battery status monitoring
One of the core functions of a BMS is real-time monitoring of the battery’s status. This includes measuring the battery’s voltage, current, temperature, and SOC (State of Charge). Using this data, the BMS assesses the battery’s health and remaining charge, ensuring it operates within a safe range. For example, if the battery voltage is too high or too low, the BMS issues an alarm and takes action, such as shutting off the charging or discharging circuit, to prevent battery damage.
Battery balancing management
In a battery pack consisting of multiple cells connected in series or parallel, the performance of each cell may vary due to factors such as manufacturing variations and usage conditions. The BMS ensures that each cell in the battery pack is charged and discharged evenly through balancing management. This can be achieved through passive balancing (such as resistor discharge) or active balancing (such as power transfer), thereby extending the battery pack’s service life.
Thermal Management
Batteries generate heat during charging and discharging, especially at high rates or high currents. The BMS monitors battery temperature and, in conjunction with cooling systems (such as fans and coolant circulation), controls the battery temperature to ensure it operates within an optimal temperature range. Good thermal management not only improves battery performance and lifespan but also prevents safety issues caused by overheating.
Communication with external systems
The BMS also needs to communicate with the vehicle control system, energy storage system, or other external devices. Through communication interfaces such as the CAN bus and RS485, the BMS can report battery status information to these external systems and receive commands from them, such as charging requests and discharge limits. This communication capability is crucial for intelligent battery management and system integration.
Security protection
A key function of a BMS is safety protection. It monitors the battery’s voltage, current, and temperature to ensure it operates within safe limits. When an abnormality is detected, such as overcharge, overdischarge, overheating, or a short circuit, the BMS immediately takes action, such as disconnecting the circuit, sounding an alarm, or activating the cooling system, to prevent battery damage or other safety incidents.
Summarize
Battery management systems (BMS) ensure safe, efficient, and reliable battery operation through real-time monitoring of battery status, balancing and thermal management, and communication with external systems. BMSs play a vital role in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and portable electronic devices, and are an integral part of modern battery technology. As battery technology continues to advance, the functionality and performance of BMSs are constantly being optimized to meet growing market demands.